
Guest Post by Geary Sikich (first posted on CERM ® RISK INSIGHTS – reposted here with permission)
Exposure to threats, hazards, and risks leads to vulnerabilities that an organization must deal with.
Commonly these are addressed via a mitigation process. Once mitigation is accomplished, often times the organization feels that the risk, threat, hazard does not need to be revisited. However, as a result of the mitigation efforts on the part of the organization, the risks, threats, hazards reconfigure and re-emerge in a different form.
In order for mitigation to be successful, it has to be a constant and ongoing process that produces a resilience to the negative effects of risks, threats, and hazards that are realized.
We can structure a matrix that depicts the three levels of mitigation and four clusters of exposure from risks, threats, and hazards. Then we can determine the potential consequences that could result from the realization of risks, threats, and hazards.
In order to simplify the context contained herein, I will refer to Risk, Threat, Hazard under the term “Risk” with the understanding of the broader context of these three unique exposure elements.
Exposure Reduction | ||||
Economic | Environmental | Social | Physical | |
Strategic | Sovereign Debt, Currency Fluctuations, “Value Chain” Exposures, Compliance Initiatives, Reputation Issues, Strategy Achievement, Profit, Goals, Objectives, Piracy, Geo-Political Issues, Economic Health, Financial Markets, Unintended Consequences of Decision Making, Risk Exposure | Pollution Control, “Value Chain” Compliance Standards, Global Environment Change, “Raw Materials” Issues, “Green” Alternatives, Unintended Consequences of Decision Making, Risk Exposure | Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Initiatives, Ethics, Standards of Care, Aging Workforce, Under Qualified Workforce, Unintended Consequences of Decision Making, Understanding Social Trends | Safety, Security, Infrastructure, Hardware Status, Information Security, Continuity of Operations, Loss Control, Technology, Unintended Consequences of Decision Making, Threat, Hazard, Risk Identification, Risk Exposure |
Operational | Cost of Operations, Compliance Violations, Goals, Objectives, Strategy Execution, Decision Communication, Seamless Vertical & Horizontal Communications, Knowledge Sharing | Pollution Control, “Value Chain” Compliance, Record Keeping, Documentation | Community Outreach, Standard of Care, Ethics, Analysis of Social Trends Against Product, Service Offerings | Hardware Run Time, Replacement Costs, Cascade Failure Impacts, Information Security, Loss Control, Threat, Hazard, Risk Identification |
Tactical | Current Budget, Term Goals & Objectives, Compliance Programs, Upward Communications, Risk, Hazard, Threat Realization Impact Costs | Pollution Control & Reporting, Environmental Compliance Programs, Threat, Hazard Identification & Impact Potential | Local Community Outreach, Local Trends | Safety, Security of Location, Perimeter Continuity, Downtime, Information Security, Loss Control, Risk, Threat, Hazard Identification |
Risk, Threat, Hazard: It’s All About the Consequences
Some facts to consider:
- Risk, Threat, Hazard are not static, they are fluid.
- Risk, Threat, Hazard probes for weaknesses to exploit.
- Risk, Threat, Hazard, therefore, can only be temporarily mitigated and never really eliminated.
- Over time Risk, Threat Hazard mitigation degrades and loses effectiveness as risk, threat, hazard mutates, creating new risk, threat, hazard realities.
Risk management requires that you constantly monitor recognized risks and continue to scan for new risks.
This process cannot be accomplished with a ‘one and done’ mindset. Risk needs to be looked at in three dimensions and perhaps even four dimensions to begin to understand the “touchpoints” and aggregation of risk, the potential to cascade, conflate and/or come to a confluence.
Ask yourself, “What is my organization’s risk absorption capacity? Where is our risk saturation point? At what point does our risk profile allow for risk deflection? At what point does our risk profile create a risk explosion for our organization?”
These four questions, all too often, never get asked when conducting investigations into risk, threat, vulnerability, business impact and/or hazard analyses. How do you begin to answer these questions?
First, you need to be open to complexity; second, you have to be able to see beyond the immediate and third, you have to embrace the dynamic nature of risk as non-static.
Risk Absorption Capacity
In researching this material, I found that most of what is presented regarding risk consists of complex mathematic equations that focus on financial exposures, insurance, probability, etc.
While this information is critically important to risk managers in quantifying risk; recognizing risk, understanding risk and the ability of an organization to withstand risk realization requires a more direct, simplified approach for risk practitioners. I propose the following general definition for simplicity.
Risk Absorption Capacity can be defined as:
“An organization’s ability to survive the uncertainty of risk realization”.
Examples abound, consider BP and the Deepwater Horizon catastrophe, the financial crisis, sovereign debt, quantitative easing, etc. Risk Absorption Capacity recognizes that not all outcomes will occur with known or estimable probabilities. The decision-maker faces an uncertain, yet recognized risk.
What the decision-maker has to understand is the capacity of the organization to shoulder the risk if it is realized. BP still faces uncertainty when it comes to the litigation surrounding the Deepwater Horizon. Europe still faces uncertainty when it comes to sovereign debt issues; even though the EU has embarked on a program of quantitative easing.
We are already seeing an increase in articles focusing on “currency wars”. When you look at your risk ledger is this an area of risk that you have analyzed or even considered with regard to your organization’s ability to survive potentially wild fluctuations in the value of the currency that dominates your balance sheets?
Recent political announcements, for example, President Obama’s budget proposal, looks at taxation of overseas money holdings of corporations such as General Electric, Microsoft, etc. If passed it could produce a windfall in tax revenue for the United States. The plan is to use this money for infrastructure improvement. The question for the affected entities will be how to address the risks created by the potential impact of the tax bill.
What if, suddenly other nations pick up on this idea and start taxing corporations for money made outside of their national boundaries? What is the risk absorption capacity to manage this risk realized? How will business strategies change and what will this do to continuity of operations?
A recent Forbes article provides an excellent example of the above. On 27 January Forbes Staff writer Maggie McGrath wrote an article entitled: “Procter & Gamble Profit, Sales Slammed By Currency Devaluations”. I have excerpted a brief example:
Procter & Gamble PG +0.32% had a rough second quarter, the company reported Tuesday morning. Due to currency devaluations around the globe, the maker of Tide, Bounty and Charmin saw its top and bottom line earnings results decline compared to the year-ago quarter and fail to meet Wall Street’s expectations. As a result of the lower-than-expected numbers as well as a prediction from P&G’s chairman that the environment will “remain challenging,” shares of P&G are sliding into negative territory in early Tuesday trading.
How many risk professionals have currency wars in their risk assessments, business impact assessment/analysis or even as a listed area for concern?
Ask yourself: “What is the cost of decision failures and sub-optimizations of resources based on denial and head in the sand mentality?”
Risk Saturation Point
At what point do we reach risk saturation? And, what exactly is meant by risk saturation?
If we break this into its component parts “risk” and “saturation” we may be able to construct a useful definition for application. According to ISO 31000, risk is the “effect of uncertainty on objectives” and an effect is a positive or negative deviation from what is expected.
This definition recognizes that all of us operate in an uncertain world and leverages this by adding that “Uncertainty (or lack of certainty) is a state or condition that involves a deficiency of information and leads to inadequate or incomplete knowledge or understanding. In the context of risk management, uncertainty exists whenever the knowledge or understanding of an event, consequence, or likelihood is inadequate or incomplete.”
Saturation is the state or process that occurs when no more of something can be absorbed, combined with, or added. In Chemistry it is the degree or extent to which something is dissolved or absorbed compared with the maximum possible, usually expressed as a percentage. Saturation: to a very full extent, especially beyond the point regarded as necessary or desirable. I propose the following general definition for simplicity.
Risk Saturation Point can be defined as:
“That point at which an organization’s capacity to absorb risk (either positive or negative) exceeds its capabilities; thereby creating an inability to sustain risk exposure”.
An example of risk saturation would be the effect of social media on decision making in a crisis. You reach a saturation point at which you can no longer process information (information overload) nor can you differentiate valid information from suspect information thereby rendering a state of decision paralysis.
Decision paralysis in a crisis can impact business survivability.
Take for example, the current state of geopolitical uncertainty in many areas of the world. The Ukraine is at a tipping point with regard to the risk of expansion of an internal conflict into a global conflict. The Ukraine is fast approaching the point of risk saturation.
This impacts any business operation with Ukrainian touchpoints. Just take a look at the airline industry to see how they have had to reroute due to the risk of being targeted by ground to air missiles.
I am sure that the airline industry had taken this into account already as they have experienced similar situations in Syria, Iraq, Kuwait and other areas of conflict; or perhaps they overlooked this until an incident occurred, read that as Malaysian Air flight 17 (shot down over the Ukraine).
Risk Deflection or Risk Explosion?
I have written about “risk buffering” and “risk parity”. In 2010 I wrote an article entitled, “Risky Business” (John Liner Review) where I began to use the term risk buffering.
Risk Buffering- recognizing that simply addressing risk does not necessarily mean mitigating risk; it means that risk is assessed, quantified, valued (what does it mean to the organization) and monitored.
Mitigating risk does not mean that risk is eliminated.
It means that the enterprise is buffered against the risk exposure. This is not a one-off or one-time process; buffering risk must be monitored constantly to ensure that you have adequate protection based on the current situation.
In an article that I wrote in 2014, entitled “Risk and the Organizational Mindset: Learn to Think like a Commodities Trader” (Continuity Central) I expanded upon the concept of risk buffering and introduced the term “risk parity”.
Risk parity is defined as an approach that focuses on the allocation of risk, usually defined by exposure, velocity, and volatility rather than allocation of assets to the risk. The risk parity approach asserts that when asset allocations are adjusted (leveraged or deleveraged) to the same risk level, risk parity is created resulting in more resistance to discontinuity events. The principles of risk parity are applied differently according to the risk appetite, goals and objectives of the organization and can yield different results for each organization over time.
I propose the following general definitions for Risk Deflection and Risk Explosion:
Risk Deflection can be defined as:
“An organization’s ability to create risk parity through risk buffering to deflect the impact of risk realization”.
Risk Explosion can be defined as:
“The impact (either positive or negative) on organization’s ability to balance risk realization resulting in greater risk awareness”.
Nassim Taleb offers the concept of “Antifragility” simply, antifragility is defined as a convex response to a stressor or source of harm (for some range of variation), leading to a positive sensitivity to increase in volatility (or variability, stress, dispersion of outcomes, or uncertainty, what is grouped under the designation “disorder cluster”).
Likewise, fragility is defined as a concave sensitivity to stressors, leading a negative sensitivity to an increase in volatility.
The relation between fragility, convexity, and sensitivity to disorder is mathematical, obtained by theorem, not derived from empirical data mining or some historical narrative. It is a priori”. Antifragility refers to systems that increase in capability, resilience, or robustness as a result of mistakes, faults, attacks, or failures.
Some examples of risk deflection and risk explosion would easily be found in the cyber world.
Cyber threats such as hacking, viruses, cyber attacks, Denial of Service (DOS) attacks are headline news today. Just do a Google search and you’ll find articles, webinars, workshops and more about cyber threats and cyber instability with the potential to disrupt global e-commerce, etc.
Organizations need to strengthen their assessment and management of cyber risks and they also need to connect the dots- that cyber threats may be related to geopolitical instability, nation-state policies for unconventional warfare and criminal activity.
Deflecting risk and capitalizing on risk explosion needs to be the next step for organizations as they begin to pursue forward-looking risk management strategies that emphasize a recognition of touchpoints, cascade potentials and the need for engagement with government, their “value chain” competitors and communities.
You need to be able to connect the dots
I have written several articles on the concept of “FutureProofing” and “Touchpoint Analysis” that have appeared in print and on the Internet.
I will summarize briefly five key assumptions that have been used as a basis to for the developmental framework of Logical Management Systems, Corp. “Futureproofing” methodology. These are:
- Assumption # 1: The modern business and government organizations represent complex systems operating within multiple networks;
- Assumption # 2: There are many layers of complexity within organizations and their “Value Chains”;
- Assumption # 3: Due to complexity, active analysis, risk buffering, risk parity, cascade analysis, etc. of the potential consequences of disruptive (positive and/or negative) events is critical to survivability;
- Assumption # 4: Actions in response to disruptive events needs to be coordinated with all touchpoints;
- Assumption # 5: Resources and skill sets are key issues that need to be recognized and addressed.
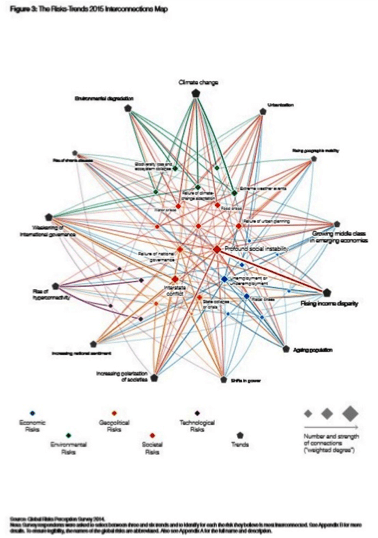
The recent World Economic Forum publication “Global Risks 2015” provides some excellent examples of connecting the dots. The figure (#3), entitled “The Risks-Trends 2015 Interconnections Map” from the WEF report is an example of what can be done when you connect the dots.
Conclusions
Risk-taking is central to the functioning of any organization.
Excessive risk taking and a simultaneous decline in the risk absorption capacity of the organization can lead to catastrophic results (i.e., the financial system and financial crisis). One can never achieve true certainty when assessing risk unless you reduce the probabilities to zero or one.
Opacity, (that is, constant uncertainty and changing factors), makes getting a clear picture of risk realities nearly impossible. In order to overcome opacity, you need to constantly monitor the risk environment. It’s all about targeted flexibility, the art of being prepared, rather than preparing for specific events.
Being able to respond rather than being able to forecast, facilitates early warning and proactive response to shifts in your market segment.
We live in a world full of consequences.
Our decisions need to be made with the most information available with the recognition that all decisions carry with them flaws due to our inability know everything.
Our focus should be on how our flawed decisions establish a context for flawed risk assessments, leading to flawed plans, resulting in flawed abilities to execute effectively.
If we change our thought processes from chasing symptoms and ignoring consequences to recognizing the limitations of decision making under uncertainty we may find that the decisions we are making have more upside than downside.
We’re limited not by the amount of risk we can identify, but by how inventive we are about how we think about risk and how much we’re willing to do to buffer against risk realization.
Here are seven identified needs for today’s risk managers:
- Techniques for identifying permanent versus cyclical changes in the external operating environment,
- Techniques for spotting and buffering risks so that the organization has the ability to leverage risk management activities for competitive advantage,
- Tools for stimulating the creation of options, particularly where change is occurring rapidly and the scope for risk management action is shifting,
- Tools for stimulating the understanding of opaque risk forces that are truly dynamic, with multiple orders of consequence effects,
- Proven tools for improving strategy, risk management, business continuity and competitive intelligence processes, breaking inertia, and jolting conventional risk management thinking.
- Techniques for generating and harnessing insights from big data about risks that customers, competitors, and suppliers present to the organization,
- Techniques for identifying and focusing the top team’s attention on new or poorly understood risks—before it is too late and the risk materialize (risk realization).
Here are five factors affecting decision-making under uncertainty:
- Interconnectedness: Opportunities for risk contagion (geographic, category, geopolitical);
- Asymmetry: Small events that can create disproportionate and unexpected effects;
- Time Compression: “Just in time” processes have little leeway with effects of risk realization being felt rapidly;
- “Noise”: Salient facts that are not noticed at the time of event (failure of critical thinking);
- Information Vetting: Misinformation or inadequately provided information that has not been properly validated can lead to greater risk exposure and skewed responses.
About the Author
Geary Sikich – Entrepreneur, consultant, author and business lecturer
Contact Information: E-mail: G.Sikich@att.net or gsikich@logicalmanagement.com. Telephone: 1- 219-922-7718.
Geary Sikich is a seasoned risk management professional who advises private and public sector executives to develop risk buffering strategies to protect their asset base. With an M.Ed. in Counseling and Guidance, Geary’s focus is human capital: what people think, who they are, what they need and how they communicate.
With over 25 years in management consulting as a trusted advisor, crisis manager, senior executive and educator, Geary brings unprecedented value to clients worldwide.
Geary is well-versed in contingency planning, risk management, human resource development, “war gaming,” as well as competitive intelligence, issues analysis, global strategy and identification of transparent vulnerabilities.
Geary began his career as an officer in the U.S. Army after completing his BS in Criminology. As a thought leader, Geary leverages his skills in client attraction and the tools of LinkedIn, social media and publishing to help executives in decision analysis, strategy development, and risk buffering. A well-known author, his books and articles are readily available on Amazon, Barnes & Noble and the Internet.
Related:
Reliability Risk Reduction Tools (article)
Reliability Management and Risk (article)
 Ask a question or send along a comment.
Please login to view and use the contact form.
Ask a question or send along a comment.
Please login to view and use the contact form.
Leave a Reply