In the article Calculating Network Reliability the lack of published analytical solution for dual-ring network reliability was highlighted. This article provides a neat solution and further challenges readers to offer their proof or prior publication reference. The solution and the author’s general proof will be presented at RAMS 2020.
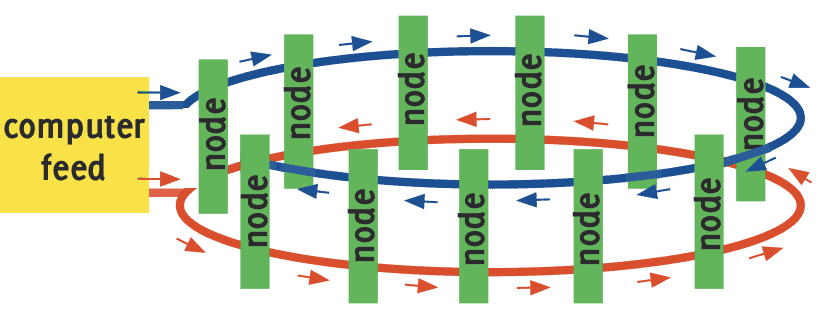
Dual-ring Network
The dual-ring network topology is described as:
- n-nodes, each node receives 2 independent data-feeds
- Each segment of the data feed, linking adjacent nodes, has a reliability R(t). All segments have equal reliability. There are n forward segments and n reverse segments.
- system is considered to be functional if at least one data-feed is received by each node.
- multiple breaks in the data-feed are allowed, provided that each node links to the computer feed by either the forward or reverse data-feeds.
- there is no cross-link between these data-feeds.
- the reliability of each node is not part of the solution – their system contribution is a simple series calculation and would be easily added to the dual-ring topology solution.
- the reliability of the main computer data feed is also not part of the requested solution – as with the nodes, its contribution is a simple series calculation.
Figure 1 illustrates the system.
Figure 1: Dual-ring topology using separate opposing-direction data feeds.
Benefits of Dual-ring Network
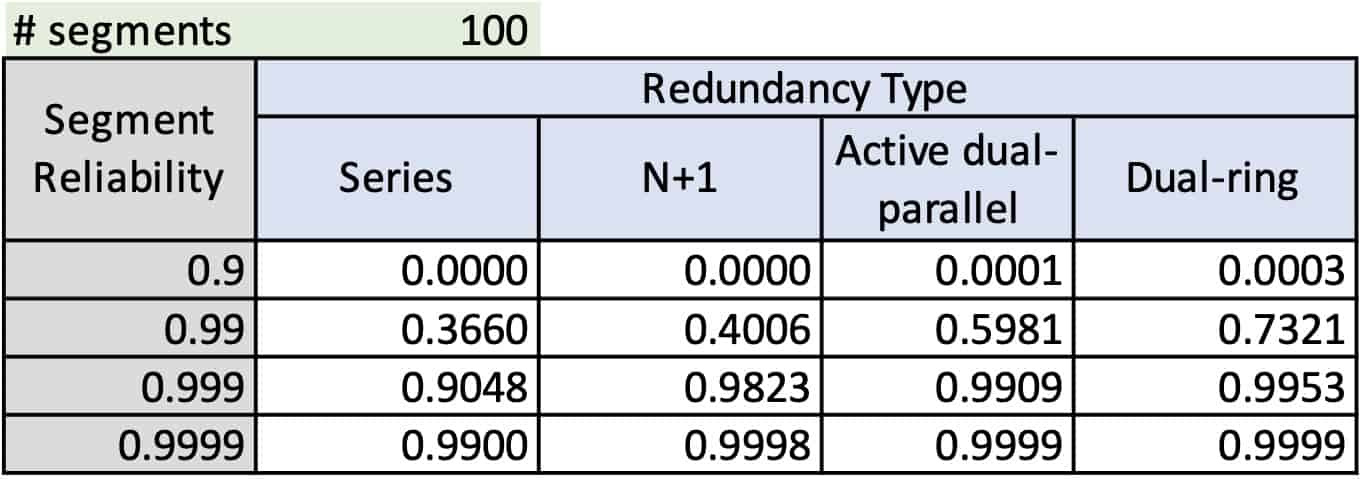
A dual ring network is no more complex than active parallel or N+1 systems. However, it offers universally higher reliability, as illustrated in Table 1.
Table 1 Illustration of alternate system reliabilities, including Dual-ring.
Analytical Solution
The analytical solution for dual-ring network reliability is:
My analytical solution and its proof will be published at RAMS 2020. However, I would welcome any other insights, particularly any reference to prior publication. Please send your comments to me, Les Warrington
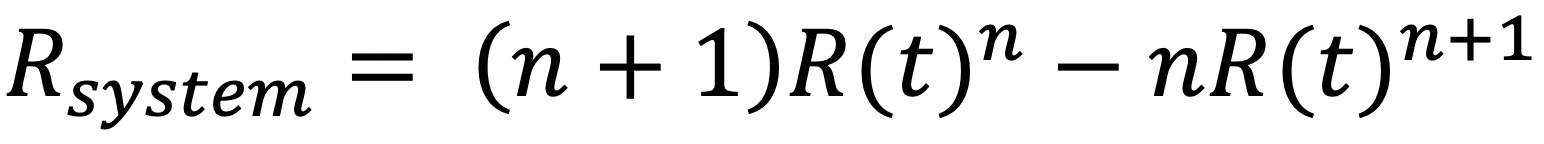
 Ask a question or send along a comment.
Please login to view and use the contact form.
Ask a question or send along a comment.
Please login to view and use the contact form.
Leave a Reply